 DIY Glycolysis
DIY Glycolysis DIY Glycolysis
DIY GlycolysisGo on to the next step.
Well done. This is the key reaction of glycolysis. You've managed to put a high energy phosphate group onto your monosacharide without spending ATP. However, you did need to use an oxidising agent, NAD+, that will need to be recycled later, and so a reduction will be required at some point.
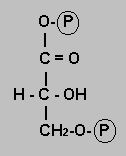
Author: Jon Maber
j.r.maber@leeds.ac.uk
Dept Biochemistry & Molecular Biology, The University of Leeds, U.K.